density control through random sampling : an architectural perspective
Paper accepted for IV02,
International Conference on Information Visualisation, July 2002, London .
Full reference:
G. Ellis and A. Dix (2002). density control through random sampling :
an architectural perspective. Proceedings of the Sixth International Conference on Information Visualisation IV02,
London, UK, July 2002, IEEE Computer Society. pp. 82-90.
http://www.hcibook.com/alan/papers/IV2002/
- See also:
- more on randomness at:
http://www.hcibook.com/alan/topics/random/
- related work on visualisation at:
http://www.hcibook.com/alan/topics/vis/
 Abstract
Abstract
Information
visualisation systems often have to cope with presenting large amounts of data.
In this paper we look at the problem of reducing the display density through
the use of random sampling. We review some of the uses of sampling and examine
density reduction techniques currently used in visualisation. We then look at
a proposed novel visualisation that utilises sampling and discuss many issues
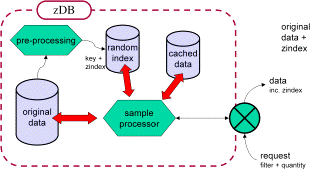
that arise. Furthermore, we propose the zDB sampling database architecture and
demonstrate how this can be used to enhance current visualisation applications.
Finally, we describe the architecture of a sampling aware application and illustrate
its advantages.
keywords: Random sampling, Visualisation, Density reduction, Large
data sets, Sampling from databases, Zoomabale interfaces
References
- Ahlberg, C. and Shneiderman, B. Visual Information Seeking: Tight Coupling of Dynamic Query Filters with Starfield Displays. Proceedings ACM Conference on Human Factors in Software, CHI '94, Boston, April 1994, ACM Press, 313-317
- Bederson, B.B and Hollan, J.D. Pad++: A Zooming Graphical Interface for Exploring Alternate Interface Physics. Proc. UIST '94, Marina del Rey, CA, November 1994, ACM Press, 17-26
- Benford, S., Snowdon, D., Greenhalgh, C., Ingram, R., Knox, I. and Brown, C. VR-VIBE: A Virtual Environment for Co-operative Information Retrieval. Proc. Eurographics 95, Blakcwell Publishers, 1995
- Chaudhuri, S., Motwani, R. and Narasayya, V. On Random Sampling Over Joins. Proc. SIGMOD '99, ???, ACM Press,1999, ??
- Chaudhuri, S., Das, G. and Narasayya, V. A Robust, Optimization-Based Approach for Approximate Answering of Aggregation Queries. Proc. SIGMOD '01, Santa Barbara , CA, May 2001, ACM Press, ??
- Dix, A. and A. Patrick. Query
By Browsing. Proc. IDS'94: The 2nd International Workshop on User Interfaces
to Databases, Lancaster, UK, April 1994. Springer Verlag: Workshops in Computer
Science. pp.236-248
- Dix, A. and Ellis, G.P. by
chance: enhancing interaction with large data sets through statistical sampling.
to be published in Proc. AVI '02, Italy, May 2002.
- Doan, K., Plaisant, C., Shneiderman, B. and Bruns, T. Interface and Data
Architecture for Query Preview in Networked Information Systems HCIL Technical
Report No. 97-09, http://www.cs.umd.edu/hcil,
1997
- G.P. Ellis, J.E. Finlay, A.S. Pollitt. HIBROWSE for Hotels: bridging the gap between user and system views of a database Proc. IDS'94 2nd International Workshop on User Interfaces to Databases, Lancaster, UK, April 1994. Springer Verlag, pp.45-58
- Fishkin, K. and Stone, M.C. Enhanced Dynamic Queries via Moveable Filters Proc. CHI '95, Denver, May 1995, ACM Press, 415-420
- Furnas, G. W. Generalized Fisheye Views. Proc. CHI '86, Boston, April 1986. ACM Press, 16-23
- Guha, S, Rastogi, R. and Shim, K. CURE: An Efficient Clustering Algorithm for Large Databases. Proc. SIGMOD '98, Seattle, June 1998, ACM Press, 73-84
- Gupta, R., Smolka, S.A. and Bhaskar, S. On Randomization in Sequential and Distributed Algorithms ACM Computing Surveys, Vol. 26, No. 1, March 1994
- Heywood, J. A dialogue Conteynyng the Nomber in Effect of all the Prouerbes in the Englishe Tongue. 1546
- Keim D. A. Pixel-oriented Visualization Techniques for Exploring Very Large Databases, Journal of Computational and Graphical Statistics, Vol. 5, No. 1, 1996, 58-77
- Kreuseler, M. and Schumann, H. Information visualization using a new Focus+Context Technique in combination with dynamic clustering of information space. Proceedings NPIV '99 (New Paradigms in Information Visualization and Manipulation), Missouri, November 1999, 1-5
- Kumar, H., Plaisant, C. and Shneiderman, B. Browsing Hierarchical Data with Multi-level Dynamic Queries and Pruning. Journal of Human-Computer Studies, 46, 1997, 103-124
- Kvamme, K.L. Randomisation methods for statistical inference in raster GIS contexts. Department of Archaeology & Center for Remote Sensing, Boston University, Boston, USA
- Lamping, J. and Rao, R. Visualizing Large Trees Using the Hyperbolic Browser. Proc. CHI '96, Vancouver, April 1996, ACM Press, 388-389
- Nakayama, K. and Silverman, G.H. Serial and Parallel Processing of Visual Feature Conjunctions. Nature 320: 264-265, 1986
- F. Olken. Random Sampling from Databases. Ph.D. dissertation, UC Berkeley, April 1993, LBL Technical Report 32883
- Pirolli, P., Schank, P., Hearst, M. and Diehl, C. Scatter/Gather browsing communicates the topic structure of a very large text collection. Proc. CHI '96, Vancouver, May 1996, ACM Press, 213220
- R. Rao, S. Card. The Table Lens: Merging graphical and symbolic representations in an interactive focus + context visualization for tabular information, Proc. CHI'94, Boston, ACM Press, 1994, pp.111117
- http://www.sas.com/products/miner/
- http://www.statsoftinc.com
- L. Tweedie, R. Spence, H. Dawkes and H. Su. Externalizing abstract mathematical models. Proc. CHI'96. ACM Press, 1996, pp.406412
- Vinson, N.G. design Guidelines for Landmarks to Support Navigation in Virtual Environments. Proc. CHI '99, Pittsburgh, May 1999, ACM Press, 278-285
- Woodruff, A., Landay, J. and Stonebraker, M. Constant Information Density in Zoomable Interfaces. Advanced Visual Interfaces '98, L'Aquila, Italy, pp.57-65.
- Woodruff, A., Landay, J. and Stonebraker, M. Constant Density Visualizations of Non-Uniform Distributions of Data. Proc. UIST '98, San Francisco, 1998, 19-28
| http://www.hcibook.com/alan/papers/IV2002/ |
Alan Dix 21/4/2002 |
 Abstract
Abstract Abstract
Abstract